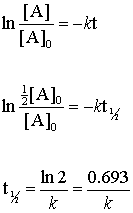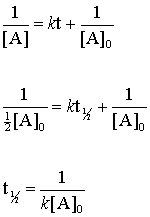half life formula for zero order reaction
A A 0 - kt. T 12 A 0 2k.
Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Video Khan Academy
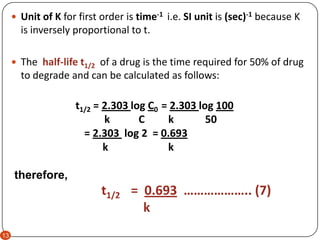
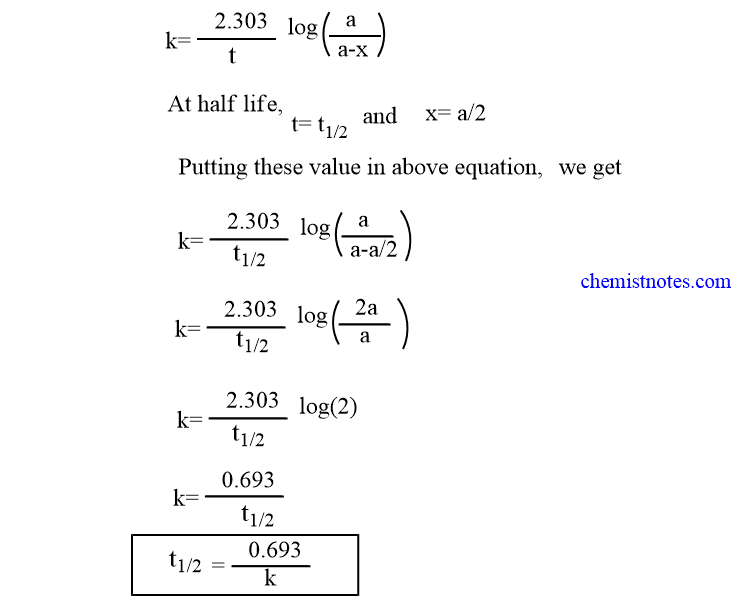
For a first order reaction t½ 0693 k and for a second order reaction t½ 1 k Ao.
. The above equation clearly shows that the half-life of the reaction is dependent on both the rate constant and the initial concentration of the reactant. When t t 12 R ½ R 0 On substituting these values in the above equation k R 0 ½ R 0 t 12. Substituting t t 12 and A t ½ A 0 in the zero-order integrated rate law yields.
From the above-integrated equation we have. The time taken for the concentration of a given reactant to reach 50 of its. The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t 12 R 0 2k.
A 0 stands for initial concentration mol. 1A n-1 1 A 0 n-1 n-1 kt. The Half-Life of Zero Order Reaction calculator computes the half-life in nuclear decay for a zero order reaction.
For a second-order reaction t12 t 1 2 is inversely proportional to the concentration of the reactant and the half-life increases as the reaction proceeds because the concentration of reactant decreases. A A 0 - kt. The formula for half-life in chemistry depends on the order of the reaction.
Given below is the half-life of a zero-order reaction. The rate constant for a zero-order reaction is measured in molL -1 s -1. A zero order reaction implies that the rate of the reaction does not depend on the concentration of the reactant.
T ½ 0693 k For a second order reaction 2A products or A B products when A B rate kA 2. T ½ 1 k A o Top. The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t12 R02k The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t12 0693k The half-life of a second-order reaction is given by the formula 1kR0.
So read on to learn more about its equation graph the half-life of a zero-order reaction and its uses. 12 A A 0 - k t 12. A A_0 kt which is the required equation.
Half-Life for a Zero-Order Reaction The integrated rate law for a zero-order reaction is given by. For the first-order reaction the half-life is defined as t 12 0693k. And for the second-order reaction the formula for the half-life of the reaction is.
Half life formula for nth order reaction. For a zero-order reaction the integrated rate law is. So one the left side this would just be two over the initial concentration of A minus one over the initial concentration of.
For a general reaction. This article focuses on zero-order reactions. Half-life of Zero-order Reactions.
For a zero order reaction the formula is t½ Ao 2k. It is to be noted that the formula for the half-life of a reaction varies with the order of the reaction. The half-life for a zero-order reaction is inversely proportional to.
Equations for Half Lives. Now replacing t with half-life t12 in the above equation. T 12 is the half-life of the reaction seconds.
K R 0 R t. T 12 12 k A 0. Because this equation has the form y mx b a plot of the concentration of A as a function of time yields a straight line.
The half-life of the reaction is denoted by t 12 and is expressed in seconds. Where A 0 Initial concentration of reactant at timet 0. An equation for zero-order half-life may be also be derived from its integrated rate law.
Half-Life of a Zero Order Reaction. The integrated rate law for the zero-order reaction A products is A_t -kt A_0. Half-Life of a Zero Order Reaction.
T ½ A o 2k For a first order reaction A products rate kA. What is the half-life equation for a second-order reaction. Graphical relations and half lives.
The half-life of a Zero-th order reaction is t A0 2kHere I derive this from the Integrated Rate LawAsk me questions. A A 0 k t AA_0-kt A A 0 k t. In the reaction BrO 3aq5Braq6H 3Br2l3H2Ol B r O 3 a q 5 B r a q 6 H 3 B r 2 l 3 H 2 O l The rate of appearance of bromine Br2 B r 2 is related to rate of disappearance of bromide ions as following Answer.
Determining a half life. Converting a half life to a rate constant. K t 12 12 A 0.
NA Product The rate law of zero order kinetics is. We have one over the initial concentration of A divided by two minus one over the initial concentration of A is equal to the rate constant k times the half-life. The rate constant for the reaction can be determined from the slope of the line which is equal to -k.
Rate law for the reaction can be written as Answer. T 12 stands for the half-life of a reaction. Remember the half-life of a reaction changes with the order of the reaction.
For a zero order reaction A products rate k. L -1 or M k stands for the zero-order rate constant. The half-life equation for a second-order reaction is t121kA0 t 1 2 1 k.

First Order Reaction Definition Example Half Life Period Chemist Notes

Kinetics Integrated Rate Law And Half Life Expression For General Nth Order Reaction N 1 Youtube

Half Life Of Zero Th 0th Order Reaction Derivation Youtube
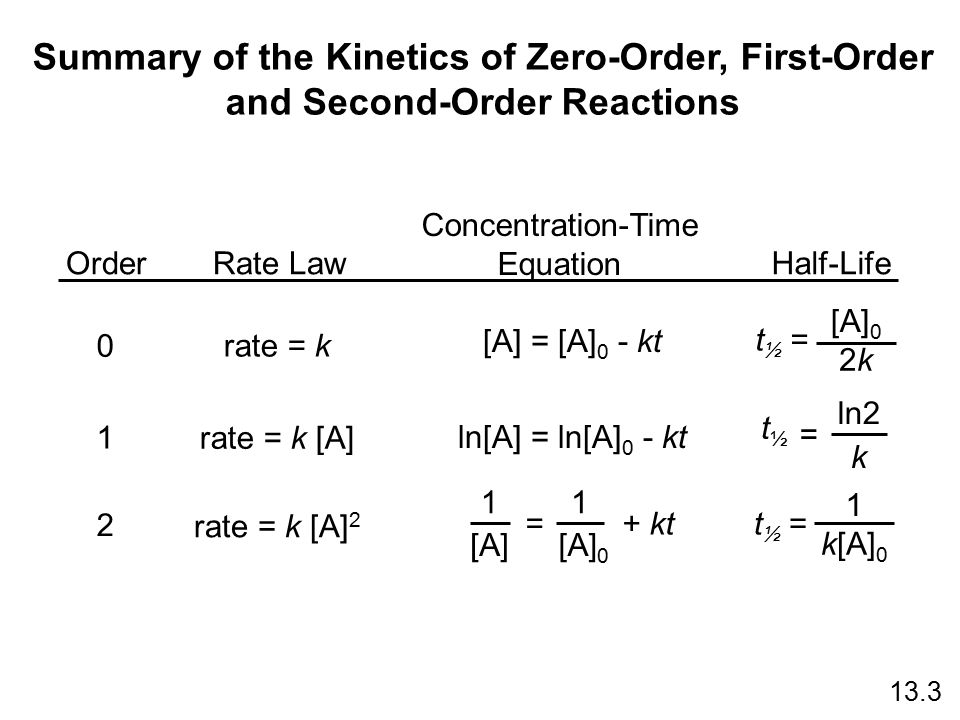
Summary Of The Kinetics Of Zero Order First Order Ppt Download

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate

Kinetics And Drug Stability Ed
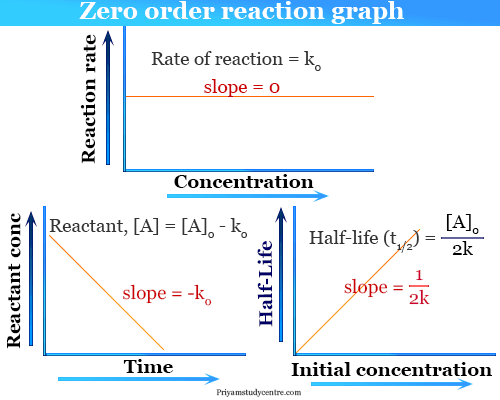
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula

Zero Order Reactions Video Kinetics Khan Academy

Zero Order Reactions Chemistry Class 12 Iit Jee Main Advanced Neet Aipmt Askiitians Youtube

Shelf Life Of Foods First Order Kinetics Youtube
Derive Half Life For Zero Order And First Order Reaction Chemistry Point

Half Life Of A Zero Order Reaction Is 250sec T75 T100 Of The Reaction Respectively In Sec Are Edurev Neet Question
First Order Reaction Derivation And It S Half Life Time Chemical Kinetics Chapter Youtube